Alternating Current
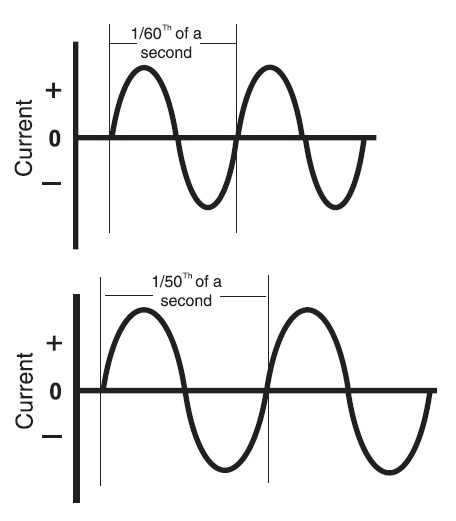
Alternating current (AC) is an electrical current that has both positive and negative half-cycles. These components do not occur simultaneously, but alternately, thus the term alternating current. Current flows in one direction during one half of the cycle and reverses direction for the other half cycle. The half cycles are called the positive half and the negative half of the complete AC cycle.
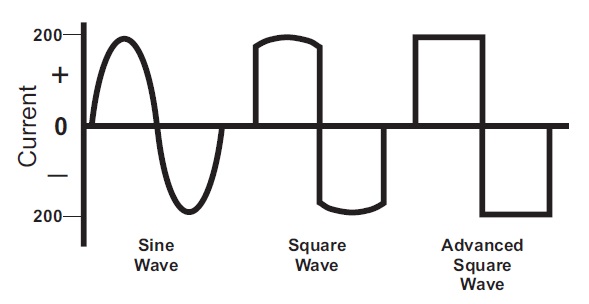
Several AC waveforms are used in welding. In addition to the sine wave, there is the square wave and the advanced square wave. What is generally called a square wave is really a modified sine wave (rounded peaks) and is the best that technology could provide on older transformer welding machines. Modern inverter welding machines are able to produce a true square wave which is referred to as an advanced square wave.
Reference: Miller – The TIG Handbook